Data Reliability for Data Lakes
这篇文章来自于Databricks工程师Michael Armbrust的演讲
1. Data Lake
The Promise of the Data Lake:
- Collect Everything
- Store it all in the Data Lake
- Data Science & Machine Learning
Michael说的比较夸张,但他意思是大部分进来的数据都是garbage,因为很难保证quality,那么一个典型的data lake项目应该是什么样的呢:
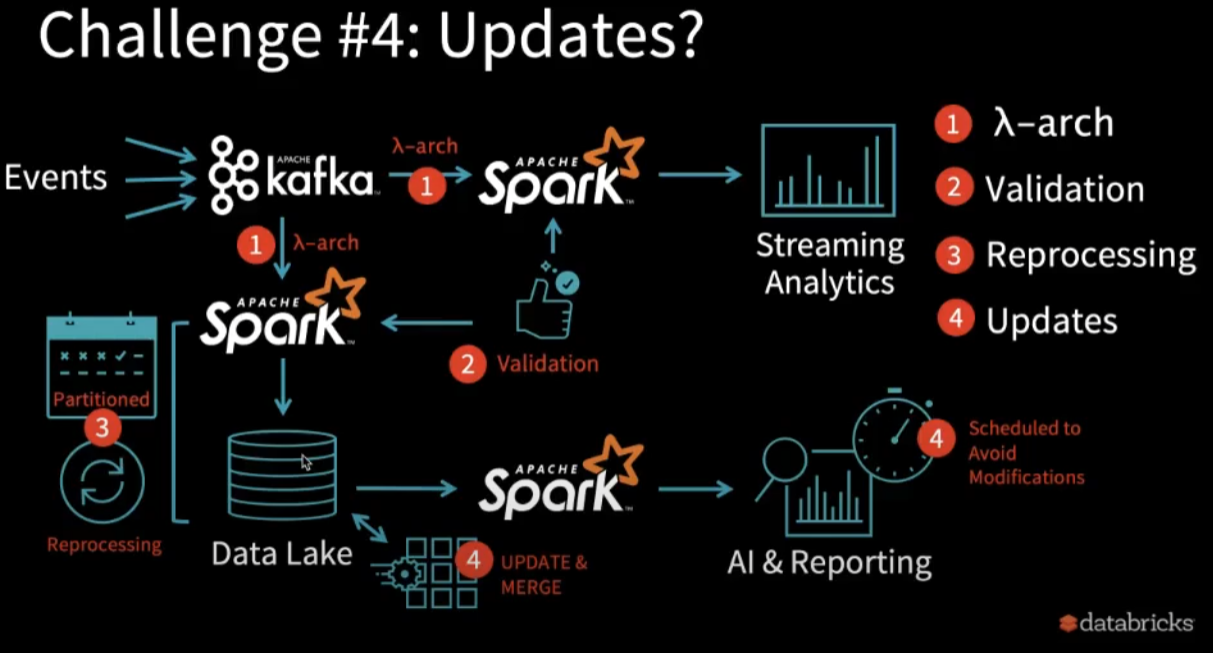
简单来说,为了解决实时分析和历史分析的问题,加入了lambda architecture;为了解决数据质量的问题,加入了validatioin;为了reprocess某些数据,加入了reprocessing;为了更新某些数据(比如为了隐藏PII)加入了update功能
Data Lake Distractions

2. Delta Lake
Delta Lake希望让上面的架构变化为如下的样子
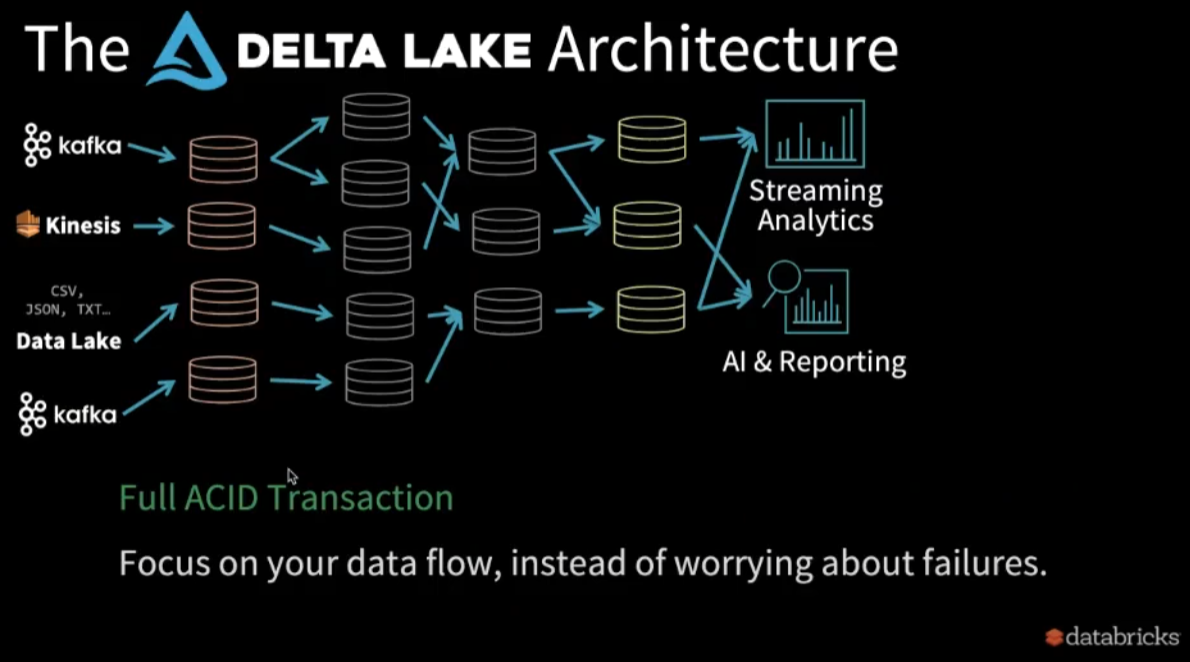
希望能够让data被增量地improve
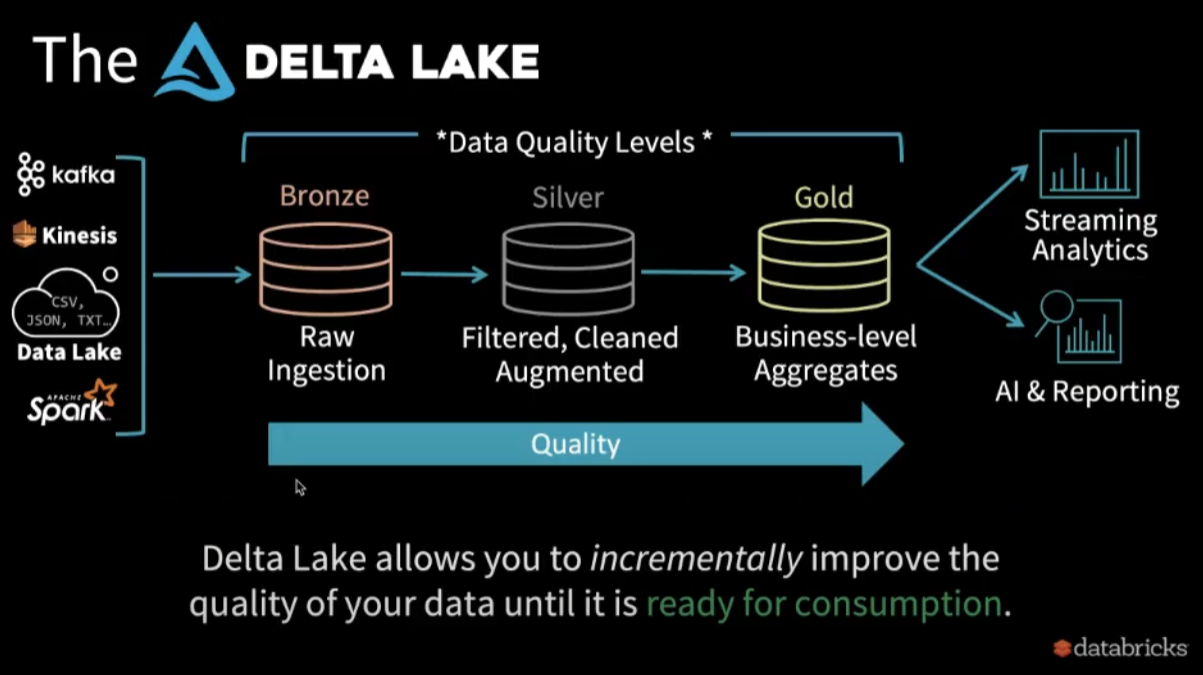
Bronze阶段
- Dumping group for raw data
- Often with long retention(years)
- Avoid error-prone parsing
Silver阶段
- Immediate data with some cleanup applied
- Querable for easy debugging
Gold阶段
- Clean data, ready for consumption
- Read with Spart or Presto
在data从Bronze -> Silver -> Gold移动的过程中,可以使用stream或者batch
3. How does Delta Lake Work
3.1. Delta on Disk
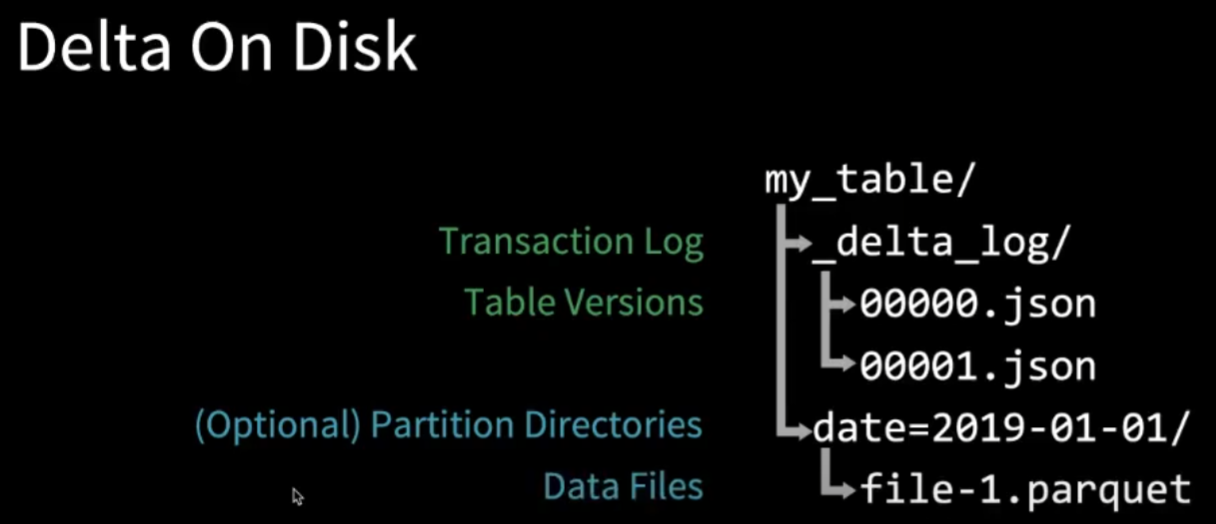
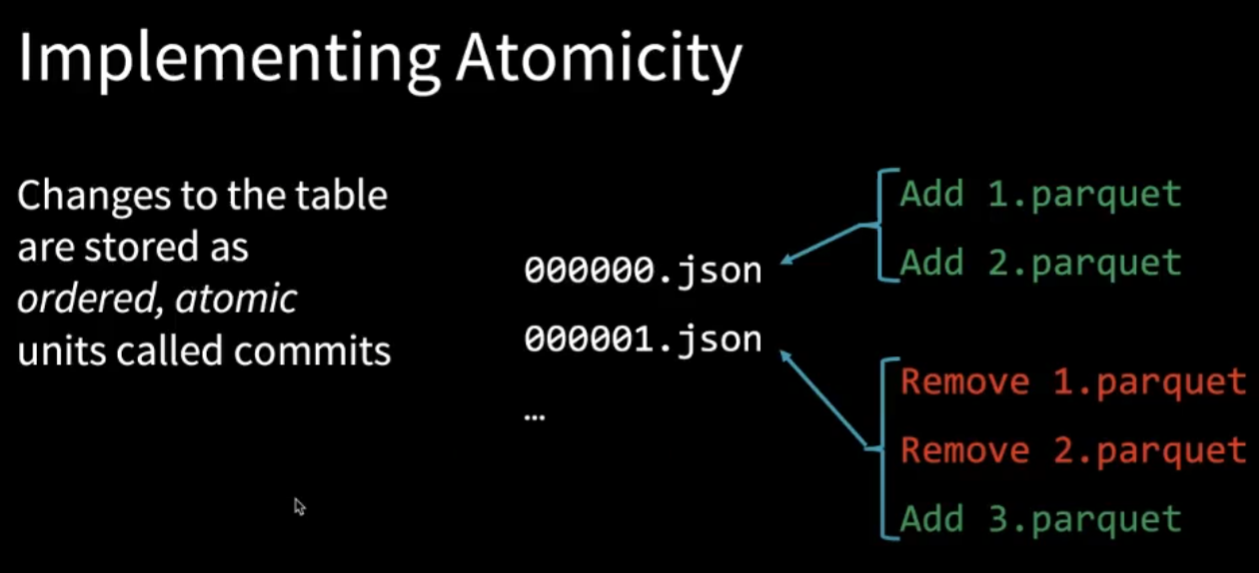
可以看到table通过一系列的json file来保存transaction和version的信息,那么怎样使用json来保存table呢?我们可以先思考下table是什么,它其实就是一系列action所造成的结果,如果我们能保存一系列的action,那么也就有了table。而且在Delta Lake中,table中的数据是否可见以能否在json中找到对应的action为准,如果找不到的话,这些parquet file会被自动garbage collected
Table = result of a set of actions
- Change Metadata - name, schema, partitioning, etc
- Add File - adds a file (with optional statistics)
- Remove File - removes a file
Result: Current Metadata, List of Files, list of Txns, Version


3.2. Handling Massive Metadata
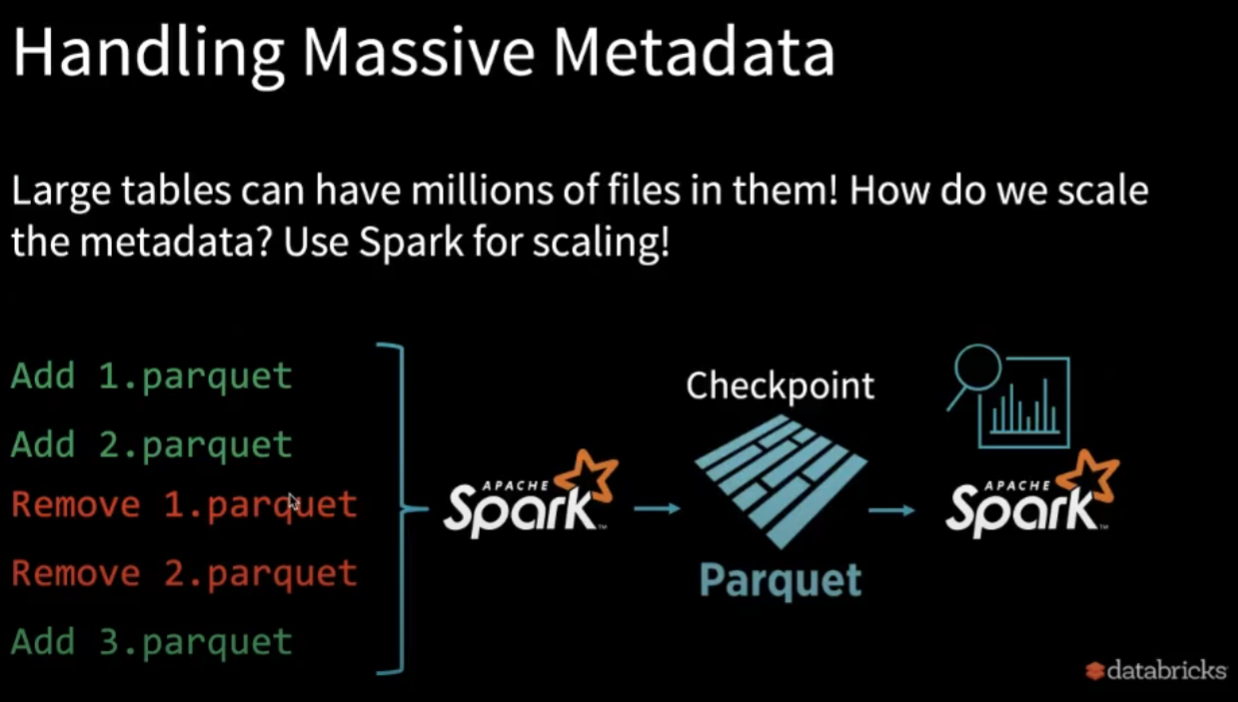
假设我们有个很大的table,有10 million的file,但我们只想query昨天的数据,首先可以写一个small Spark query来filter metadata来找到与query相关的file,接着使用另一个Spark query来process那些file